Research

Glycans serve a critical role in cell-cell communication and function through their interaction with other biomolecules, such as proteins.
Proteoglycans (PGs) and their glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains play a prominent role in a biological system. PGs are among the most structurally complex of the glycoconjugates and are involved in signaling and cell-cell interaction.
Glycomics is a field that is a logical offshoot of the fields of genomics and proteomics and is considered as a sub-discipline of metabolomics.
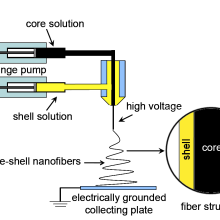
Nano-biotechnology is a new field, lying at the convergence of biotechnology and nanotechnology, which integrates biomaterials and synthetic materials to prepare novel nano-scale and micron-scale materials, devices and processes.

